We are moving into a time when the extraordinary advances that have
been made in the fields of nanotechnology, neurology, psychology,
computer science, telecommunications and artificial intelligence will be
used by governmental authorities to control the population? Already,
governments around the world are using the threat of “terror” as an
excuse to watch us, track us, scan all of our electronic communications
and force us to endure “security measures”
that are so extreme that
even George Orwell could have never dreamed them up. So what is going
to happen one day when some crazed individual actually does set off a
weapon of mass destruction in a major city? The temptation to use these
emerging technologies to control the public will become almost
irresistible. At this point “mind control” is still a dirty word to
many, but after the next couple of “9/11 style events” the general
population will be crying out for something to be done to ensure their
security. When society experiences a complete and total meltdown in the
years ahead, governments around the world will be tempted to do just
about anything, including using mind control, to restore order. That is
why some of the most recent advances in the field on nanotechnology are
so chilling.
In particular, what a team of researchers at the University at
Buffalo have discovered is truly alarming. The following is an excerpt
from their recent news release….
Clusters of heated, magnetic nanoparticles targeted to cell
membranes can remotely control ion channels, neurons and even animal
behavior, according to a paper published by University at Buffalo
physicists in Nature Nanotechnology.
Using nanoparticles to remotely control animal behavior?
It doesn’t take a doctorate to understand the implications of such a technology.
What if “nanobots” that had the capacity to control human minds were
programmed to search out and attach themselves to key areas of the human
brain?
Such “nanobots” would be far too small to even be seen by the human
eye, and people could become “infected” with these creatures without
even knowing it.
Hordes of these nanobots could be released into the atmosphere or in
public areas and infect thousands (or even millions) and nobody might
even realize it.
If governments could find a way to use nanobots to remotely control
the minds of the general population, a mass mind control program could
be implemented without the general public even realizing what is going
on.
Yes, this is just how scary this technology is.
But it gets even worse.

You see, when it comes to nanotechnology we are dealing with something far more dangerous than we can even imagine.
For example, if something goes horribly wrong and we develop
speed-breeding self-assembling nanobots that get out of control,
they could theoretically devour all life on Earth in fairly short order.
Think of the scene at the end of the recent Keanu Reeves movie
entitled “The Day The Earth Stood Still” and multiply it by about a
million.
But even if such a scenario never plays out, the mind control potential of nanotechnology is bad enough.
Not that other mind control technologies aren’t equally as dangerous.
The truth is that all kinds of mind control technologies are being developed.
Video game makers are busy developing games that you control not with a joystick or a gamepad but rather
with your brain waves. So could such a technology someday be used in reverse?
Of course most people by now have heard of MK-ULTRA and other mind
control programs that were developed by the CIA and other U.S.
government agencies.
The U.S. government insists that all such programs have been discontinued.
But are they telling the truth?

And what are other governments around the world developing in secret?
There are other mind control technologies out there that are incredibly dangerous as well.
In fact, there are many who suggest that electromagnetic waves could
potentially be used to control thoughts and influence behavior. Think
of what just one terrorist could do with such technology.
But one of the most disturbing developments of all is the
increasingly rapid merger of men and machines that is now taking place.
People have been looking for ways to stay more “connected” to the
Internet for a long time, and now some are actually suggesting that we
should find a way to directly connect our brains to the Internet.
A recent article on the website of the Science Channel put it this way….
What if it were possible to connect your brain to the Internet,
either wirelessly or through a cable, download digital information at
high speed, and then translate it automatically into a chemical form
that could be stored by your brain cells as memory?
The same article explained what some of the benefits from such a connection might be….
If you could pump data directly into your gray matter at, say, 50
mbps — the top speed offered by one major U.S. internet service
provider — you’d be able to read a 500-page book in just under
two-tenths of a second.
But what about the dangers?
What if the Internet could end up controlling you?
Or what if a really bad computer virus was downloaded into your brain?
Think it can’t happen?

Well, British researcher Mark Gasson infected an RFID chip in his hand
with a computer virus and found that the virus-infected chip implanted in his hand was able to contaminate external systems.
Imagine if that started happening on a large scale.
And someday it might.
Especially as we approach the time that futurists refer to as “The Singularity”.
The Singularity is hard to define, but basically many futurists
believe that the merging of man and technology is happening at such an
increasingly rapid pace that at some point the new “transhumans” will
become virtually incomprehensible to normal human beings. The idea is
that by merging man and machines, transhumans will become smarter,
stronger, healthier and more powerful than we could have ever dreamed
possible.
So will men and computers fully merge someday?
Let’s hope not.

But even now, an increasing number of people are developing ways to tag humans with RFID microchips.
In fact, one company called Somark has developed a breakthrough in chipless RFID ink. Their
“RFID tattoos” are applied using a geometric array of micro-needles and a reusable applicator with a one-time-use ink capsule.
So how easy is it to apply one of these RFID tattoos?
Well, it takes about 5 to 10 seconds to tattoo an animal or a human.
Once the tattoo has been applied, an RFID reader can read it from up
to four feet away.
But who needs a tattoo? IBM has actually announced that they have developed a “bar code reader”
that can read your DNA.
Very frightening stuff.
The truth is that the vast majority of people do not want their DNA scanned and they do not want RFID chips implanted into them.
But RFID chips are being implanted into people more than ever before.
The reality is that microchipping of humans
is becoming quite commonplace in the United States. For example,
RFID implants are being implanted in thousands of elderly Americans living with Alzheimer’s disease who
are at risk of wandering off and getting lost. In addition, RFID chips
are being implanted into many people who are chronically ill so that
doctors can access their medical information quickly in an emergency.
The truth is that there are some people who are quite eager to be
chipped. One columnist named Don Tennant recently published an article
entitled
“Chip Me – Please!” in
which he expressed his excitement that Barack Obama’s new health
law may include coverage for RFID chip implants that contain patient
identification and health information. In fact, Tennant makes the
following stunning admission in his article….
All I can say is I’d be the first person in line for an implant.
So is this our future?
Is everyone going to be taking lots of microchips and implants?
Will there come a day when microchips and implants are made mandatory?
After all, what better way to truly identify someone? Identification
cards and papers can be forged or can get lost. But if you implant
someone with a microchip how are they going to lose that?
However, we all know that the potential for abuse of all of the
technologies mentioned in this article is just too great. If someday a
tyrannical regime gets a hold of these kinds of ultra-powerful
technologies the results could be absolutely nightmarish.
Original:
http://endoftheamericandream.com/archives/mind-control-scientists-have-discovered-how-to-use-nanoparticles-to-remotely-control-behavior




















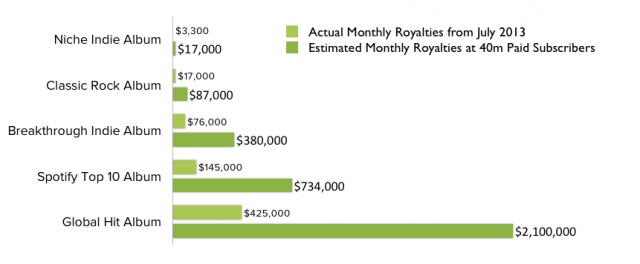
 Ever
since the rise of file-sharing sites during the past decade, a few
recurring themes have been pushed by the world’s largest record labels.
Alongside claims of astonishing losses and irreparable damage being done
to the entire industry, one notable defeatist mantra raised its head
time and again.
Ever
since the rise of file-sharing sites during the past decade, a few
recurring themes have been pushed by the world’s largest record labels.
Alongside claims of astonishing losses and irreparable damage being done
to the entire industry, one notable defeatist mantra raised its head
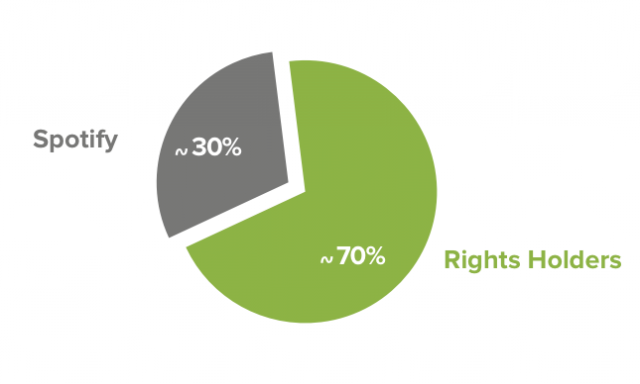
time and again. “A
key part of this [success] has been in ensuring that Spotify has a free
[ad supported] tier. By offering this free tier, Spotify is able to
compete with piracy on cost and bring music consumers into the legal
framework,” the company notes.
“A
key part of this [success] has been in ensuring that Spotify has a free
[ad supported] tier. By offering this free tier, Spotify is able to
compete with piracy on cost and bring music consumers into the legal
framework,” the company notes.